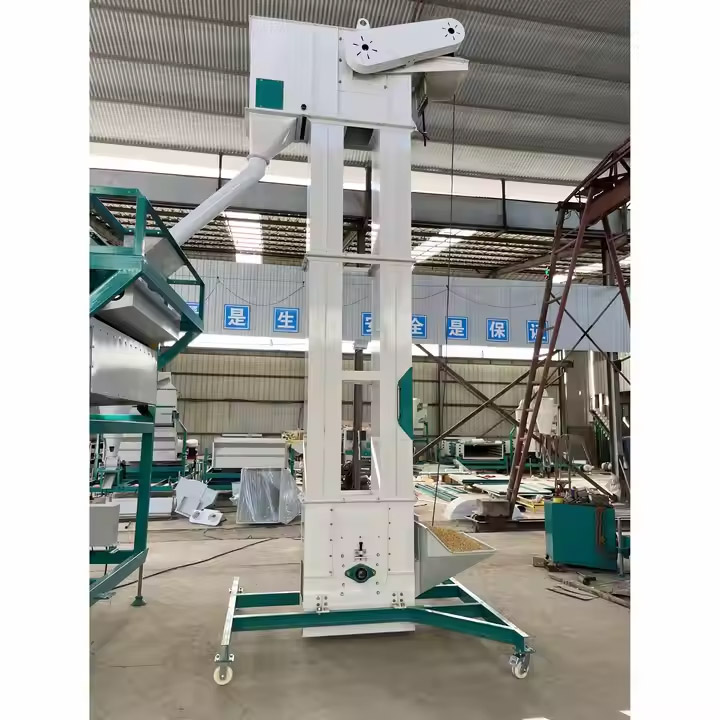
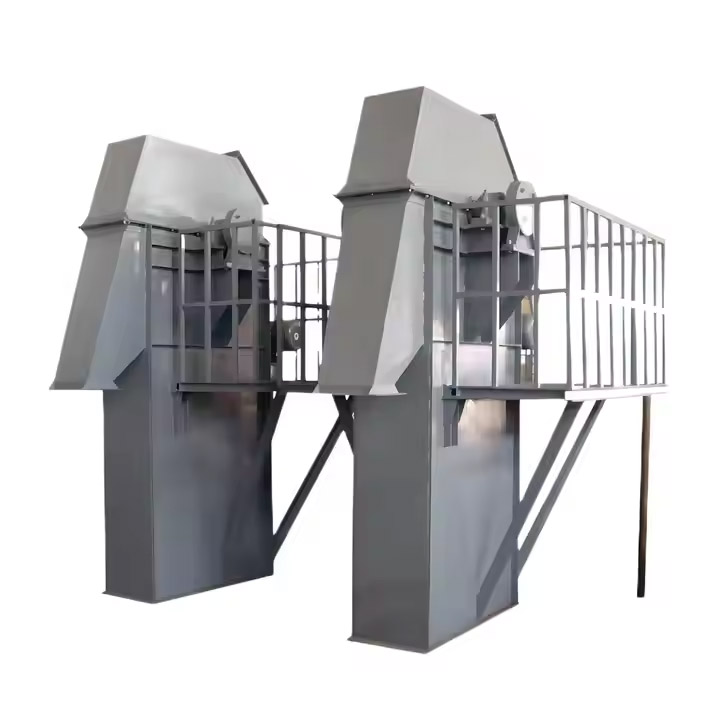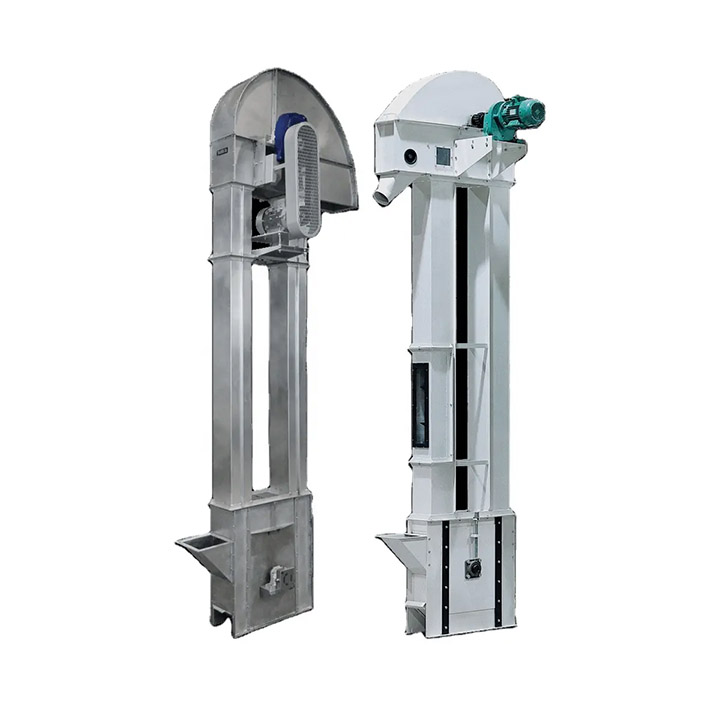
Coal Conveying Bucket Elevator
Used for vertical lifting of bulk materials such as coal
Lifting height: 10-80 meters
Conveying capacity: 50-800 t/h
Bucket capacity: 5-50 liters
Operating speed: 0.8-2.5 m/s
What is Coal Conveying Bucket Elevator?
Coal Conveying Bucket Elevator is a mechanical equipment specially used for vertical or inclined conveying of bulk materials such as coal and coke. It lifts coal from low to high through a bucket fixed on a chain or belt, and is widely used in coal, power, metallurgy, chemical industry and other industries. Bucket elevator has the characteristics of high efficiency, stability and good sealing, which can meet the needs of large-scale coal transportation.
What is Coal Conveying Bucket Elevator used for?
The main purpose of Coal Conveying Bucket Elevator is to convey coal and other bulk materials vertically or obliquely, including:
1. Coal transportation: lifting coal from the ground or coal storage yard to high coal storage bins, boilers or conveying equipment.
2. Coke transportation: in the metallurgical industry, it is used for the lifting and transportation of coke.
3. Other bulk materials: vertical transportation of materials such as ore, limestone, gypsum, etc.

What industries is Coal Conveying Bucket Elevator used in?
1. Coal Industry: Used for coal transportation in coal mines, coal washing plants, thermal power plants and other places.
2. Power Industry: Used for coal lifting in coal-fired power plants to transport coal to boilers for combustion.
3. Metallurgical Industry: Used for lifting and conveying materials such as coke and ore.
4. Chemical Industry: Used for the transportation of coal chemical raw materials.
5. Building Materials Industry: Used for the lifting of building materials such as limestone and gypsum.

How does Coal Conveying Bucket Elevator work?
A Coal Conveying Bucket Elevator works by using a continuous loop of buckets attached to a belt or chain to vertically lift bulk coal. The coal is fed into the elevator's boot (bottom section), where the buckets scoop it up. As the belt/chain rotates, the loaded buckets travel upward, discharge coal at the top through centrifugal or gravity force, then return empty to repeat the cycle. Key components include drive motors, tensioning systems, and dust-proof enclosures to ensure efficient, enclosed coal transport for industries like power plants and mining.
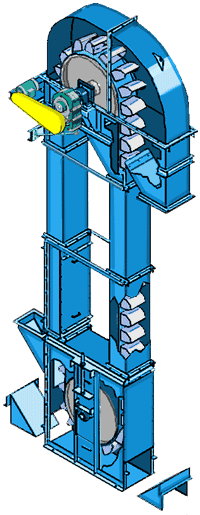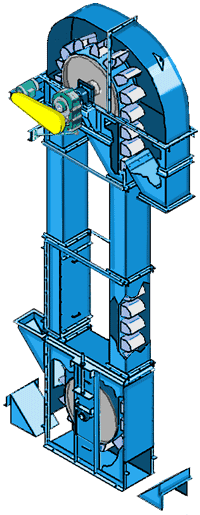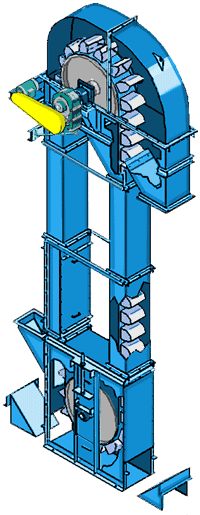
What are the advantages of Coal Conveying Bucket Elevator?
1. Efficient transportation: It can continuously and stably transport large amounts of coal, with a lifting height of tens of meters.
2. Good sealing: It adopts a closed structure to reduce the spillage of coal dust and meet environmental protection requirements.
3. Strong adaptability: It can transport coal of different particle sizes and humidity and adapt to various working conditions.
4. Compact structure: It occupies a small area and is suitable for places with limited space.
5. Smooth operation: It adopts chain or belt drive, which runs smoothly and has low noise.
What components does Coal Conveying Bucket Elevator consist of?
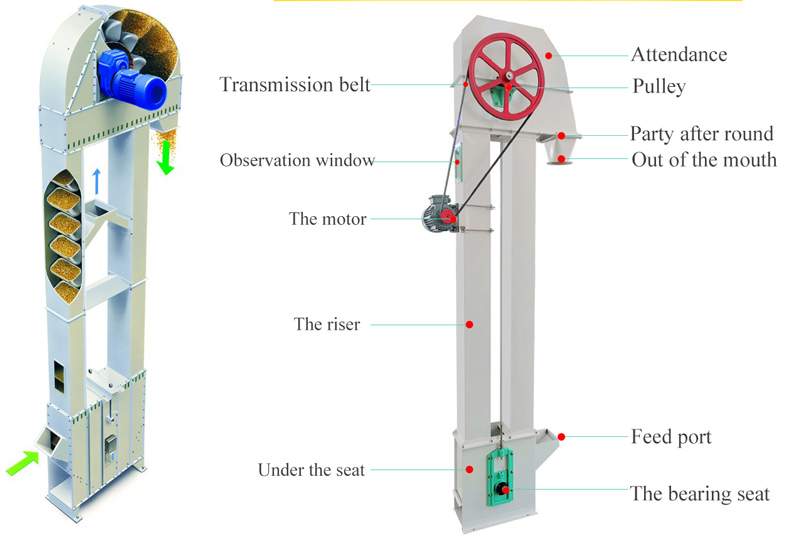
1. Head
- Driving device: including motor, reducer, coupling, etc., to provide power.
- Head roller: drives the chain or belt to drive the bucket to run.
- Discharge port: the outlet where coal is discharged from the bucket.
2. Tail
- Tail roller: guides the chain or belt to maintain tension.
- Feed port: the entrance where coal enters the bucket.
- Tensioning device: adjusts the tension of the chain or belt to prevent slipping.
3. Bucket - Material: usually made of wear-resistant steel plate or plastic.
- Shape: designed according to the characteristics of the conveyed material, common ones are deep bucket, shallow bucket, pointed bottom bucket, etc.
- Fixing method: fixed to the chain or belt by bolts or welding.
4. Chain or belt
- Chain: suitable for heavy load and high temperature environment, common ones are roller chain and plate chain.
- Belt: Suitable for light load and high speed environment, common ones are rubber belt and nylon belt.
5. Casing
- Material: Usually made of steel plate, lined with wear-resistant material inside.
- Structure: Closed design to prevent dust from spilling and protect the environment.
6. Support structure
- Column: Support the entire equipment and keep it stable.
- Beam: Connect the columns to enhance the overall rigidity.
7. Safety device
- Speed monitor: Monitor the speed of the chain or belt to prevent slipping or breaking.
- Anti-reverse device: Prevent the equipment from reversing when it stops.
- Emergency stop switch: Stop quickly in an emergency.
8. Control system
- Electrical control cabinet: Contains control elements such as start, stop, and speed regulation.
- Sensor: Monitor the operating status of the equipment, such as temperature, vibration, material level, etc.
Coal Conveying Bucket Elevator Customer Case
| Case | Application scenario | Lifting height | Lifting amount | Key features |
| Coal mine to power plant: | Used to transport coal mined from coal mines vertically to the coal storage bunker of power plant boilers to optimize the fuel supply process | 30m | 200 t/h | Using heavy-duty chain traction, wear-resistant and high-temperature resistant, suitable for long-term continuous operation; equipped with dust-proof sealing design to reduce dust pollution during coal transportation |
| Port loading and unloading | Used for port coal loading and unloading, lifting bulk coal from cargo ships to conveyor belts, and then transferring to storage areas | 25m | 150 t/h | NE series adapts to high humidity environments to prevent coal agglomeration; low failure rate design, suitable for high-intensity operations |
| Coking plant pretreatment | Used for lifting and grading coal before coking in coking plants to ensure the quality of coke | 40m | 100 t/h | High temperature resistant chain (can withstand 250°C), low breakage rate |
How to Select Coal Conveying Bucket Elevator?
Selecting the right bucket elevator for coal conveying requires analysis of coal properties, lifting height, capacity, motor configuration, and operational conditions. Here’s a structured approach:
1. Coal Characteristics
| Property | Impact on Selection | Recommended Solution |
| Moisture Content | Wet coal may clog; dry coal generates dust | → Sealed design (NE-type) for dust prevention; anti-clogging buckets |
| Particle Size | Lumps vs. fines affect bucket filling efficiency | → Deep buckets for lumps; scoop-type for fines |
| Abrasiveness | Coal with high silica wears buckets/chains faster | → Wear-resistant steel buckets + hardened chains |
| Temperature | Hot coal (e.g., from drying) requires heat resistance | → Heat-resistant chains (TH-type, up to 250°C) |
2. Lifting Height
| Height Range | Suitable Elevator Type | Key Considerations |
| < 20m | Belt-driven (TD-type) | Low power, cost-effective |
| 20–40m | Chain-driven (NE-type) | Balanced strength & speed |
| > 40m | Heavy-duty chain (TH-type) | Reinforced structure to handle load |
Note: Taller elevators need intermediate bearings to prevent belt/chain sagging.
3. Capacity
| Capacity | Bucket Size & Speed | Motor Power (Example) |
| < 50 t/h | Small buckets, 1–1.2 m/s | 7.5–15 kW |
| 50–200 t/h | Medium buckets, 1.5 m/s | 18.5–45 kW |
| > 200 t/h | Large buckets, 2 m/s | 55–110 kW |
Formula:
Motor Power (kW)≈Capacity (t/h)×Height (m)60×Efficiency (0.7–0.8)
Motor Power (kW)≈60×Efficiency (0.7–0.8)Capacity (t/h)×Height (m)
4. Motor Configuration
| Requirement | Motor Type | Advantages |
| Standard duty | 4-pole AC motor | Reliable, low maintenance |
| Variable speed | VFD-controlled motor | Adjust flow to match demand |
| Harsh environments | Explosion-proof (Ex d) | Safe for coal dust zones |
| High torque | Gearmotor + reducers | Smooth start for heavy loads |
Summary: Coal Bucket Elevator Selection Table
| Factor | TD-Type (Belt) | NE-Type (Chain) | TH-Type (Heavy Chain) |
| Best For | Dry, fine coal | General-purpose | Abrasive/hot coal |
| Max Height | ≤30m | ≤50m | ≤60m |
| Max Capacity | 150 t/h | 300 t/h | 200 t/h (high-temp) |
| Maintenance | Low | Moderate | High (chain wear) |
Final Tips:
For powdery coal: Use enclosed NE-type to reduce dust.
For high-capacity plants: Prioritize NE/TH-types with VFD motors.
For ports/mines: Opt for corrosion-resistant coatings.
Consult manufacturers for custom designs (e.g., anti-explosion, wear liners).



