Cement Conveying Bucket Elevator
Mechanical equipment used for vertical or inclined transportation of cement raw materials, cement clinker, cement powder
Lifting capacity: 15-800 cubic meters per hour
Lifting height: 40 meters
Material temperature: below 250℃
It can be used to vertically lift cement powder, cement clinker, ore, limestone, coal powder and other powdery, blocky and bulk materials.
What is Cement Conveying Bucket Elevator?
Cement Conveying Bucket Elevator is a mechanical equipment used for vertical or inclined conveying of powdered, granular or small pieces of materials. It is widely used in cement, building materials, chemical, metallurgical and other industries. It lifts materials from low to high through a bucket fixed on a chain or belt. It has the characteristics of high efficiency, stability and good sealing.

What are the types of Cement Conveying Bucket Elevator?
| Type | TD/D belt bucket elevator | TH/HL chain bucket elevator | NE plate chain bucket elevator | TB type plate chain bucket elevator (old-fashioned, gradually replaced by NE type) | Z type bucket elevator (rotating bucket type) |
| Traction component | Tape (temperature resistant 60°C, steel rope tape can reach 80°C) | Forged chain (high temperature resistant 250°C) | Plate chain (wear-resistant and impact-resistant) | Plate chain (similar to NE type, but with lower efficiency | Used for "horizontal-vertical-horizontal" transportation, such as cement packaging line; the transportation capacity can reach 100m³/h, and the lifting height is ≤100m |
| Applicable materials | Powdered and small granular cement, bulk density <1.5t/m³, low abrasiveness. | Cement clinker, slag, etc. with high abrasiveness | Powdered, granular cement and raw materials with moderate abrasiveness | Block clinker, slag, etc. | |
| Features | Using centrifugal or mixed unloading, stable operation, low noise; conveying capacity can reach 500m³/h, lifting height ≤40m268; suitable for conveying raw materials and finished cement in cement plants. | Using gravity or mixed unloading, suitable for materials with high specific gravity; conveying capacity can reach 365m³/h, lifting height ≤50m; sturdy structure, suitable for high-temperature materials (such as rotary kiln clinker). | Using gravity-induced unloading, the conveying capacity is large (15~800m³/h); the lifting height can reach 50m, which is suitable for large-scale cement production lines; compared with the chain type, it runs more smoothly and has low maintenance costs. | Suitable for low-speed and heavy-load conditions, but has been replaced by the NE series | |
| Selection | Powdered cement (such as raw materials, finished cement) - TD/D type (belt type); high-temperature clinker, slag - TH/HL type (chain type); large-volume cement plants - NE type (plate chain type); special layout requirements - Z type (rotating bucket type) | ||||
What industries can Cement Conveying Bucket Elevator be used in?

- Cement manufacturing: used for the transportation of raw materials and finished products in the cement production process.
- Building materials: used for the lifting of building materials such as limestone, gypsum, sand and gravel.
- Chemical industry: used for the transportation of chemical raw materials, fertilizers, plastic particles, etc.
- Metallurgical industry: used for the lifting of materials such as ore, mineral powder, coke, etc.
- Grain processing: used for the vertical transportation of granular materials such as grains and feed.
What are the advantages of Cement Conveying Bucket Elevator?

1. Efficient conveying: It can continuously and stably convey a large amount of material, and the lifting height can reach tens of meters.
2. Good sealing: It adopts a closed structure to reduce dust spillage and meet environmental protection requirements.
3. Compact structure: It occupies a small area and is suitable for places with limited space.
4. Smooth operation: It adopts chain or belt drive, which runs smoothly and has low noise.
5. Easy maintenance: simple structure, easy maintenance and repair.
6. Strong adaptability: capable of conveying a variety of materials, including powder, granular and small pieces.
How does Cement Conveying Bucket Elevator work?
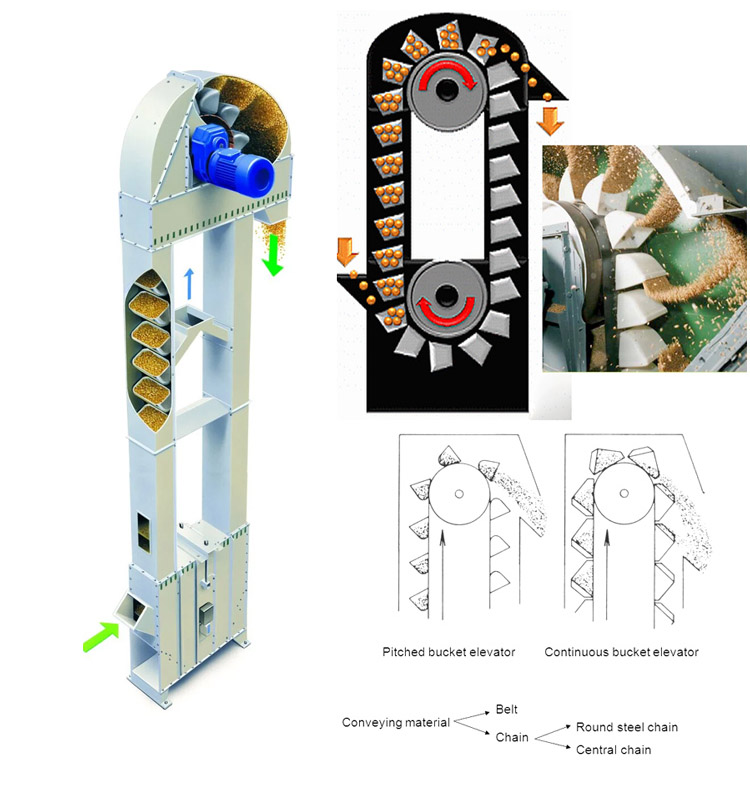
1. Loading: The material enters from the bottom feed port, and through the continuous movement of the hopper, the material is scooped up and loaded into the hopper.
2. Lifting: The hopper rises vertically or obliquely along the track of the elevator with the movement of the chain or belt.
3. Unloading: When the hopper reaches the top, the material is discharged from the hopper by gravity or centrifugal force and enters the discharge port.
4. Cycle: The empty hopper continues to move downward and returns to the bottom for the next loading, forming a continuous working cycle.
Cement Conveying Bucket Elevator Parameters
| Model | TH160 | TH200 | TH250 | TH315 | TH400 | TH500 | TH630 | |||||||||||
| Bucket | ZH | SH | ZH | SH | ZH | SH | ZH | SH | ZH | SH | ZH | SH | ZH | SH | ||||
| Delivery volume m³/h | Normal type | 15 | 25 | 18 | 29 | 31 | 48 | 35 | 60 | 60 | 94 | 75 | 118 | 114 | 185 | |||
| Upgraded | - | - | - | - | - | - | 46 | 80 | 80 | 125 | 100 | 157 | 152 | 246 | ||||
| Bucket | Bucket width mm | 160 | 200 | 250 | 315 | 400 | 500 | 630 | ||||||||||
| Bucket capacity L | 1.2 | 1.9 | 1.5 | 2.4 | 3.0 | 4.6 | 3.75 | 6.0 | 5.9 | 9.5 | 9.3 | 15.0 | 14.6 | 23.6 | ||||
| Bucket distance mm | Normal type | 500 | 512 | 688 | ||||||||||||||
| Upgraded | - | 384 | 516 | |||||||||||||||
| Chain | Round steel (diameter×pitch)mm | 14×50 | 18×64 | 22×86 | ||||||||||||||
| Number of rings | Normal type | 9 | 7 | 7 | ||||||||||||||
| Upgraded | - | 5 | 5 | |||||||||||||||
| Bucket running speed m/s | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.5 | |||||||||||||||
| Main sprocket pitch diameter mm | 300 | 365 | 520 | 630 | 710 | 800 | 900 | |||||||||||
| Spindle speed r/min | 69.71 | 63.22 | 44.11 | 42.5 | 37.6 | 35.8 | 31.8 | |||||||||||
| Particle size mm | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 50 | 60 | |||||||||||
| Equipment model | Lifting capacity range (t/h) | Applicable materials |
| Small | 10 - 50 | Cement, fly ash, grain |
| Medium | 50 - 200 | Limestone, gypsum, fertilizer |
| Large | 200 - 500 | Ore, coke, sand and gravel |
- Lifting height: usually 10 meters to 50 meters, can be customized according to needs.
- Conveying capacity: the conveying volume per hour ranges from a few tons to hundreds of tons.
- Hopper capacity: designed according to material characteristics and conveying volume, the capacity ranges from a few liters to tens of liters.
- Driving power: depending on the lifting height and conveying volume, the power ranges from a few kilowatts to tens of kilowatts.
- Running speed: usually 0.8 m/s to 1.6 m/s.
- Material: the hopper and shell are usually made of wear-resistant steel plate or stainless steel, and the chain or belt is made of high-strength material.
What are the structural components of Cement Conveying Bucket Elevator?
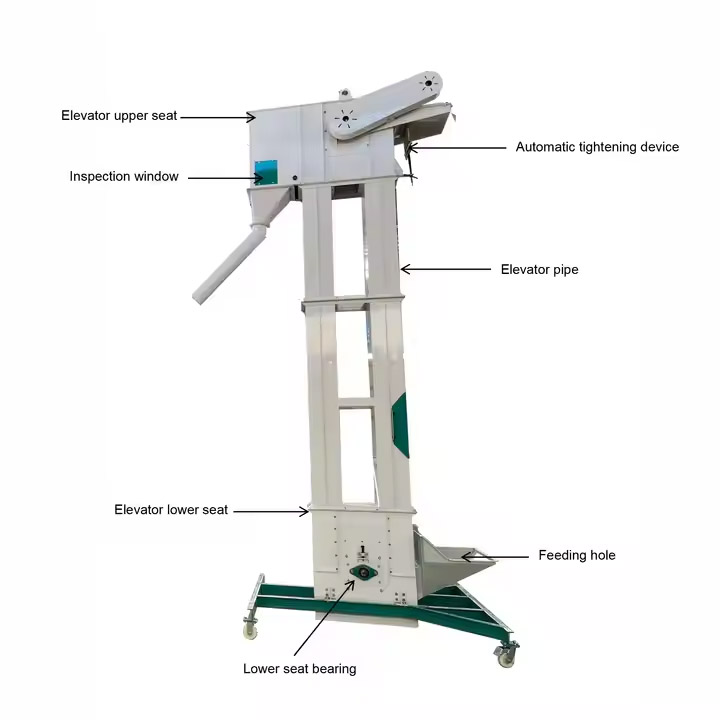

1. Driving device: including motor, reducer and drive wheel, providing power to move the chain or belt.
2. Hopper: fixed on the chain or belt, used for loading and lifting materials.
3. Chain or belt: as the support and transmission part of the hopper, driving the hopper up and down.
4. Shell: closed structure to prevent material spillage and dust diffusion.
5. Feed port: located at the bottom, the material enters the hopper through the feed port.
6. Discharge port: located at the top, the material is discharged from the hopper through the discharge port.
7. Tensioning device: used to adjust the tightness of the chain or belt to ensure smooth operation.
8. Safety device: including overload protection, emergency shutdown, etc. to ensure safe operation of the equipment.
Cement conveying bucket elevator customer case
| Customer Cases | A cement plant in the Philippines - TGD bucket elevator | A building materials plant in Pakistan - stainless steel bucket elevator | Sinoma Tianshan Cement - New anti-accumulation bucket elevator |
| Application scenarios | Used in large cement production lines to vertically transport cement clinker and finished cement. | Used in vertical transportation of powdered materials (such as raw cement) in cement plants. | Cement production lines can solve the problem of material accumulation in traditional elevators and improve transportation efficiency. |
| Lifting capacity | 30 tons/hour | 6 cubic meters/hour | 15 cubic meters/hour |
| Lifting height | 45m | 2.8 meters | 15m |

How to select a cement conveying bucket elevator?
Selecting the right bucket elevator for cement conveying requires careful consideration of cement properties, lifting height, capacity, power system, and other factors. Below is a detailed analysis for optimal selection.
1. Cement Characteristics (Material Properties)
Cement properties significantly impact elevator choice:
| Parameter | Impact on Selection | Recommended Elevator Type |
| Powder (e.g., Portland cement) | Low abrasiveness, easy to convey | TD/D-type (belt-driven) |
| Granular (e.g., clinker, slag) | High abrasiveness, heavy | TH/HL-type (chain-driven) |
| Moisture content | Risk of clogging, sticking | NE-type (sealed design, anti-clogging) |
| Temperature | Hot clinker (>150°C) | High-temp chain (TH-type, heat-resistant) |
| Explosive dust risk | Need for explosion-proof motors | ATEX-certified models |
2. Lifting Height (Vertical Conveying Distance)
The required lifting height determines structural strength and drive power:
| Lifting Height (H) | Suitable Elevator Type | Notes |
| < 20m | TD/D-type (belt) | Economical, low maintenance |
| 20m – 40m | NE-type (chain) | High stability, medium load |
| > 40m | TH/HL-type (heavy-duty chain) | Reinforced structure for long-distance lifting |
| Horizontal + Vertical (Z-type needed) | Z-type (chain-driven) | For complex layouts (e.g., packing plant) |
3. Capacity (Tons/Hour or m³/Hour)
The required throughput affects bucket size, speed, and motor power:
| Capacity (Q) | Bucket Size & Speed | Motor Power (kW) Example |
| < 50 m³/h | Small buckets, low speed (~1 m/s) | 5.5 – 11 kW |
| 50 – 200 m³/h | Medium buckets, moderate speed (~1.5 m/s) | 15 – 30 kW |
| > 200 m³/h | Large buckets, high speed (~2 m/s) | 37 – 75 kW (heavy-duty) |
Formula for Power Estimation:
P=Q×H×ρ×g3600×ηP=3600×ηQ×H×ρ×g
QQ: Capacity (t/h)
HH: Lifting height (m)
ρρ: Bulk density (~1.5 t/m³ for cement)
ηη: Efficiency (~0.8 for belt, ~0.7 for chain)
4. Drive System (Motor & Transmission)
The power system must match load and duty cycle:
| Drive Type | Advantages | Best For |
| Gearmotor (Direct Drive) | Compact, efficient | Small/medium elevators (TD/NE-type) |
| Chain + Sprocket (Heavy-Duty) | High torque, durable | Large TH/HL-type for clinker |
| Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) | Speed control, energy-saving | Precise flow adjustment needed |
| Explosion-Proof Motor | Safe in dusty environments | Cement silo filling |
5. Additional Selection Factors
Dust Control: Sealed elevators (NE-type) reduce pollution.
Maintenance Access: Removable panels for easy cleaning.
Material of Construction:
Stainless steel for corrosive environments.
Wear-resistant steel for abrasive clinker.
Summary: Cement Bucket Elevator Selection Table
| Criteria | TD/D-type (Belt) | NE-type (Chain) | TH/HL-type (Heavy Chain) |
| Best for | Powder cement | General-purpose | Hot/clinker/slag |
| Max Height | ≤40m | ≤50m | ≤60m |
| Capacity | Up to 500 m³/h | Up to 800 m³/h | Up to 400 m³/h |
| Temp Limit | ≤80°C | ≤120°C | ≤250°C |
| Maintenance | Low | Medium | High |
Final Recommendation
For fine cement powder: TD/D-type (low cost, low maintenance).
For mixed/hot materials: NE-type (balanced performance).
For high-temperature clinker: TH/HL-type (heavy-duty).



