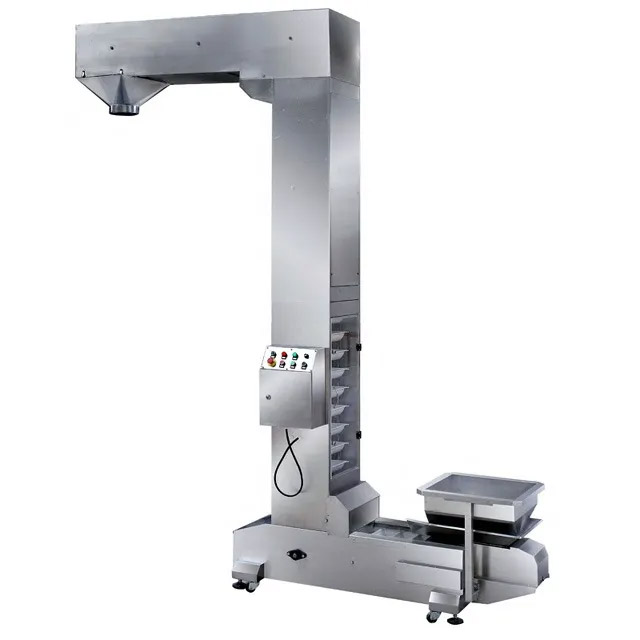
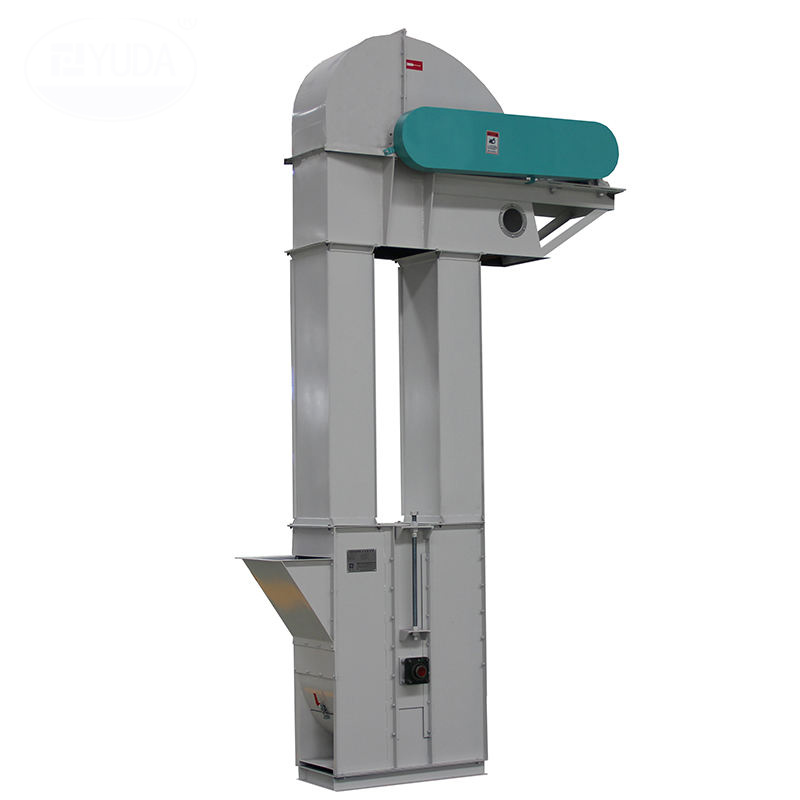
Bucket elevator for salt materials
vertically conveying salt materials, including raw salt, refined salt, and industrial salt.
| Lifting height | 3 m - 90 m |
| Conveying capacity | 15 m³/h - 1,000 t/h |
| Bucket capacity | 2.5 L - 52.2 L |
| Material temperature | ≤ 250 ℃ (special design) |
| Drive mode | Motor drive |
| Applicable materials | Salt, grain, cement, ore, etc. |
| Sealing performance | High to prevent materials from spilling or getting wet |
What is Bucket Elevator for Salt Materials ?
Bucket Elevator for Salt Materials is a device used for vertical transportation of bulk materials, especially for granular, powdery or small block materials such as salt, grain, cement, ore, etc. For salt materials, bucket elevators need to have the characteristics of corrosion resistance, moisture resistance and efficient transportation to ensure stable operation in harsh environments.
What is the purpose of the bucket elevator for salt materials?
1. Vertical transportation: lift salt materials from low to high, suitable for warehousing, production lines or packaging.
2. Efficient transportation: through the continuous operation of the bucket design, large quantities of salt materials can be quickly transported.
3. Reduce loss: The sealing design prevents salt materials from spilling or getting wet during transportation.
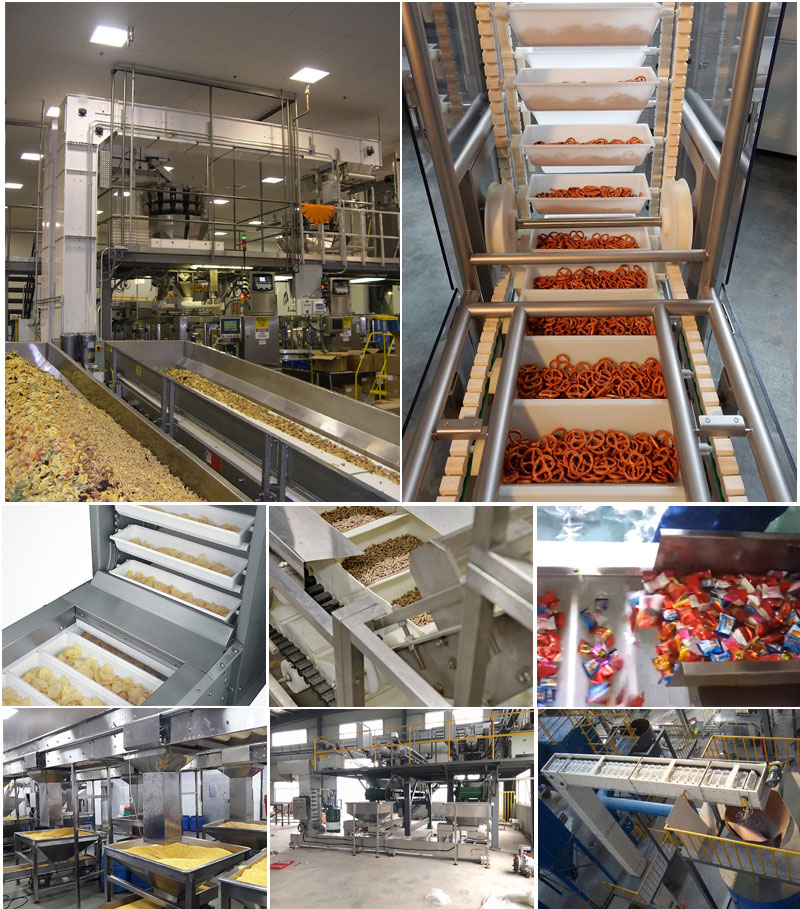

What are the applications of bucket elevator for salt materials?
1. Food processing industry: used for the transportation of materials such as salt and condiments.
2. Chemical industry: transport industrial salt, sodium chloride and other chemical raw materials.
3. Mining and metallurgy: used for material lifting after salt mining.
4. Agriculture: Transporting salt components in feed additives.
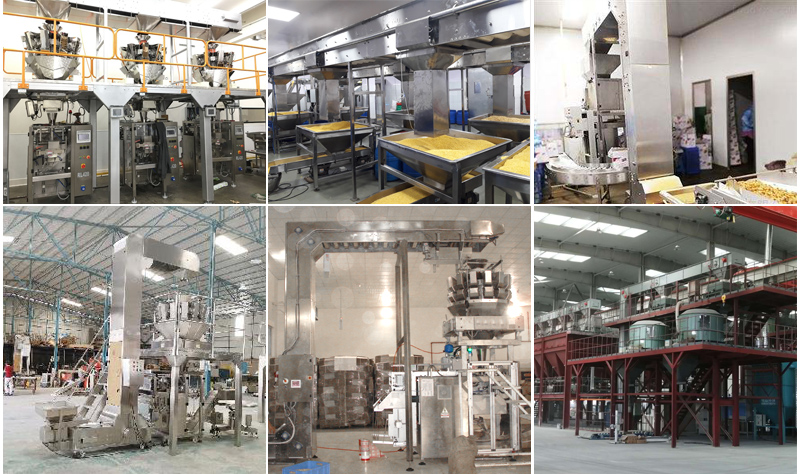

How does Bucket Elevator for Salt Materials work?
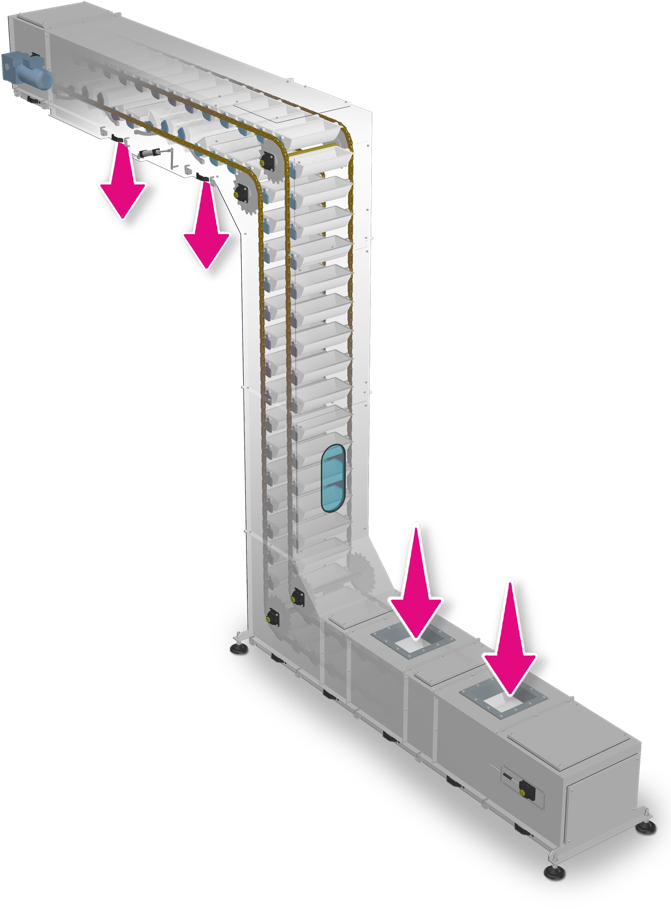
1. Material loading: Salt materials enter the bottom bucket of the elevator through the feed port.
2. Vertical lifting: The bucket is driven by a chain or belt and lifted vertically to the top.
3. Material unloading: At the top, the bucket dumps the material to the discharge port through centrifugal force or gravity.
4. Circulation operation: The empty bucket returns to the bottom and continues to load materials, forming a continuous cycle.
Bucket Elevator for Salt Materials Parameters
| bucket volume | 1.8L | 3.6L | 6.5L |
| bucket material | pp | ss304 | ABS |
| body material | mild steel | stainless steel | --- |
| NO.S of discharge port | single | muti-discharge port | --- |
| output | 4-6m3/h | 6.5-8m3/h | 5.5-12m3/h |
| voltage(v) | 220v/240v/as you need | 380v/415v/440v/as you need | as you need |
| speed | adjustable | ||
| conveying capacity | 3-10m3/h | ||
Bucket Elevator for Salt Materials Structure
1. Head: Contains the drive device and the discharge port.
2. Tail: Contains the feed port and tensioning device.
3. Bucket and chain/belt: The bucket is used to load the material, and the chain or belt is used to drive the bucket.
4. Shell: Sealed design to prevent material spillage and external contamination.
5. Safety device: Including limiter, anti-reversal device and temperature detection device.

Bucket Elevator for Salt Materials Customer Cases
| Application Scenario | Amount of improvement | Raise height |
| Vertical elevation of fine salt aggregates in food and chemical industries, where ATEX compliance and stainless steel construction are required for corrosion resistance. | Designed for powders and small granules (up to 5 mm particle size), with a high-efficiency belt system for continuous material flow. | 45m |
| A pharmaceutical company uses a fully automatic spiral packaging machine to package tablet drugs with high precision to ensure compliance with GMP standards | 185 m³/h | 40m |
| Ideal for salt processing where material temperatures reach up to 250°C, such as in mineral refining or chemical production. | 30t/h | 50m |
1. Food processing plant: A salt production company uses bucket elevators to transport raw salt from the warehouse to the production line, achieving efficient and pollution-free material transportation.
2. Chemical plant: A chemical company uses corrosion-resistant bucket elevators to transport industrial salt, solving the problems of material moisture and equipment corrosion.

Bucket Elevator for Salt Materials Selection
1. Material characteristics: Select the appropriate bucket material (such as high-density polyethylene or stainless steel) according to the particle size, humidity and corrosiveness of the salt material.
2. Conveying capacity: Select the appropriate bucket capacity and lifting speed according to production needs.
3. Environmental requirements: In humid or corrosive environments, choose moisture-proof and corrosion-resistant designs.
4. Safety standards: Ensure that the equipment meets relevant industry standards, such as ATEX explosion-proof certification.
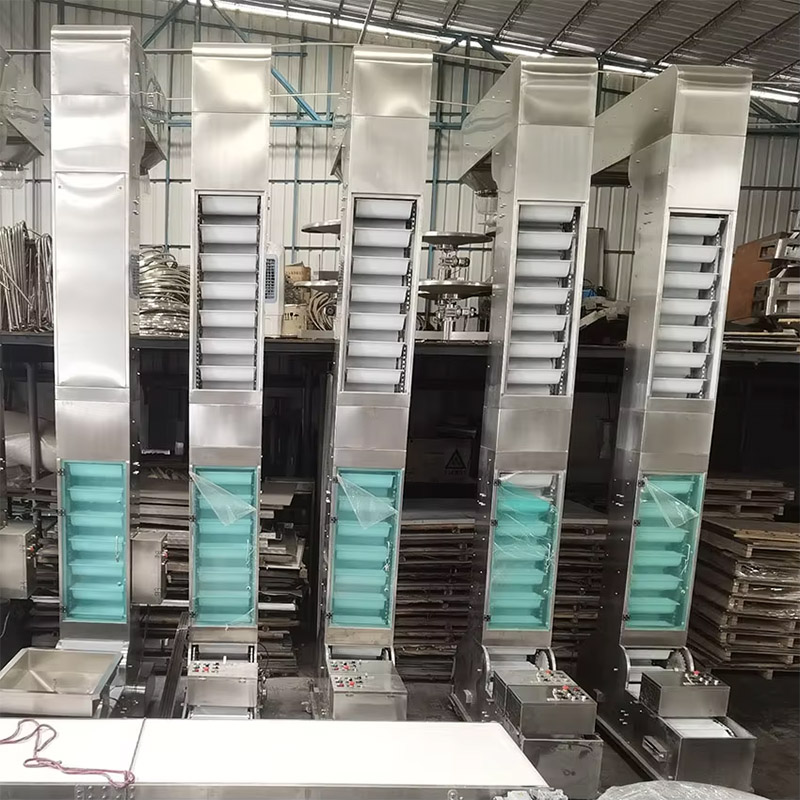

 Stainless Steel Bucket Elevator
Stainless Steel Bucket Elevator
