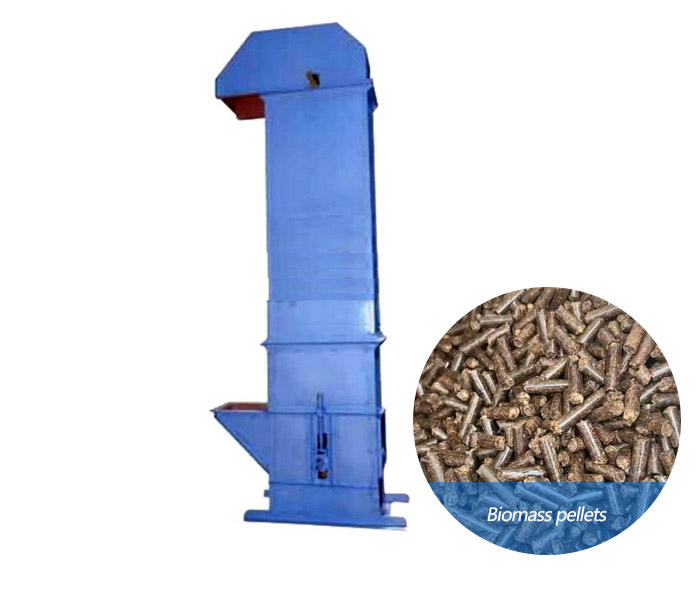
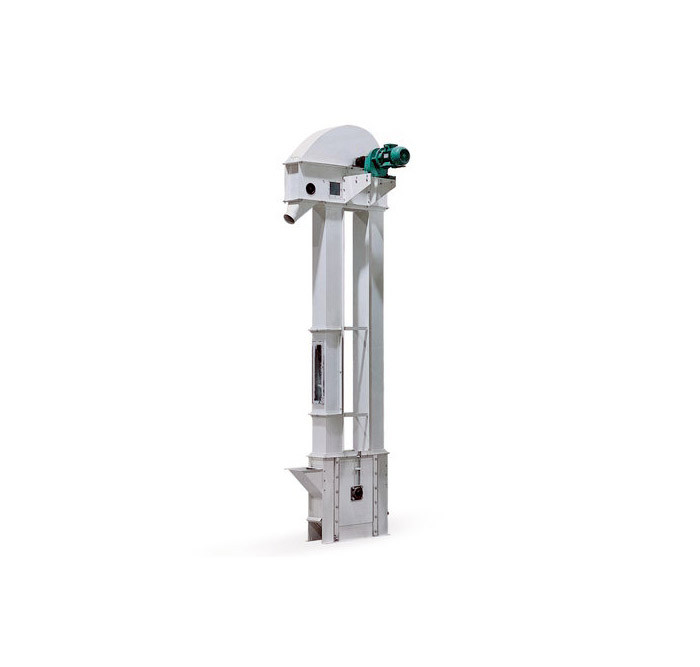
Biomass pellet bucket elevator
Equipment for lifting biomass pellets from low to high
| Lifting height | 5-50 meters |
| Conveying capacity | 5-100 tons/hour |
| Hopper capacity | 0.5-20L |
| Motor power | 1.5-30kW |
| Applicable materials | biomass pellets, wood pellets, feed pellets, chemical pellets, etc. |
Looking for a reliable bucket elevator for your biomass pellet plant? Our biomass pellet bucket elevator is built to transport wood pellets and other biomass materials with minimal breakage, optimized for high throughput and long-term efficiency.
What is biomass pellet?
First, we need to understand what biomass pellets are. Biomass pellets are solid fuels made from agricultural and forestry waste (such as wood chips, straw, rice husks, etc.) through crushing, drying, compression and other processes. It has the following characteristics:

Environmental protection: It produces fewer pollutants when burned and is a clean energy source.
Renewable: The raw materials are widely available and highly renewable.
High calorific value: It has high combustion efficiency and can provide stable heat energy.
Easy to store and transport: It has high density and small volume, which is easy to store and transport.
What is Biomass pellet bucket elevator?
The biomass pellet bucket elevator is a device specially used for vertically conveying biomass pellets (such as wood chip pellets, straw pellets, feed pellets, etc.). It lifts pellet materials from low to high through a hopper fixed on a belt or chain, and is widely used in biomass energy, feed processing, agriculture and other fields.

What types of Biomass pellet bucket elevators are there?
Belt bucket elevator: Uses belt as traction member, suitable for conveying small and medium-sized particles.
Chain bucket elevator: Uses chain as traction member, suitable for conveying larger particles or heavier materials.
Chain bucket elevator: Uses chain as traction member, suitable for conveying high-temperature or highly abrasive materials.

Why choose bucket elevator for conveying biomass pellets?
1.Automated transportation: Replace manual handling, improve production efficiency and reduce labor intensity.
2. Continuous operation: Able to achieve continuous and stable material transportation to meet the continuity requirements of the production line.
3. Vertical lifting: Able to vertically lift biomass pellets to storage bins, combustion furnaces and other equipment for subsequent processing.
4. Reduce material loss: Closed transportation reduces the scattering and loss of materials during transportation.
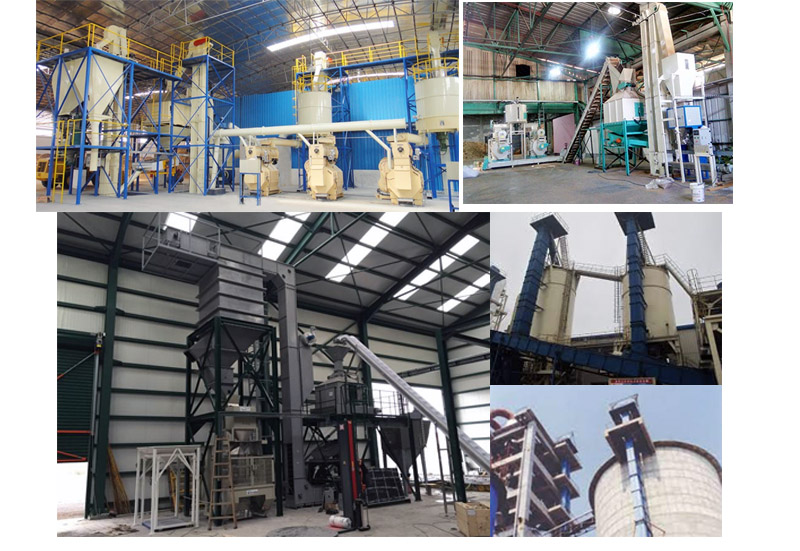
What are the applications of biomass pellet bucket elevator?
Biomass power plant: transport biomass pellets to the combustion furnace for power generation.
Biomass heating system: transport biomass pellets to the heating boiler to provide heat energy.
Biomass pellet production line: transport biomass raw materials to the press to produce pellets.
Biomass energy: used for the transportation of biomass fuels such as wood pellets and straw pellets.
Feed processing: transport feed pellets to packaging or storage equipment.
Agriculture: used for vertical transportation of crop pellets (such as corn, soybeans, etc.).
Chemical industry: transport granular chemical raw materials.

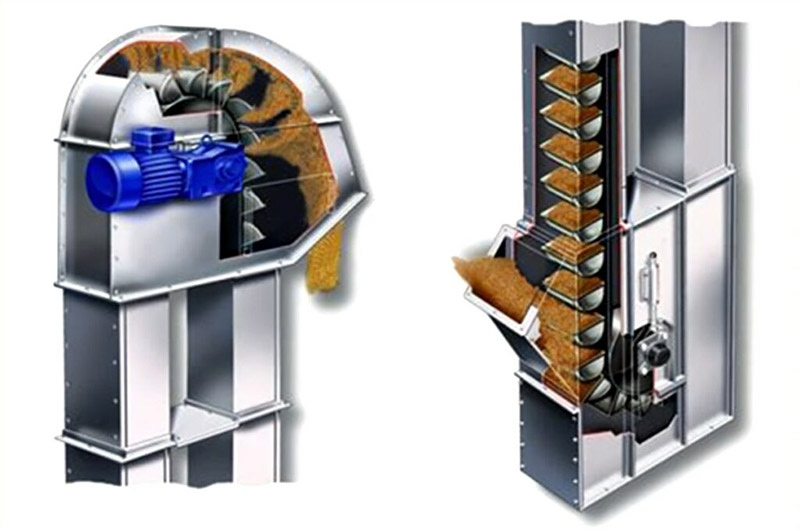
How does the Biomass pellet bucket elevator work?
The bucket elevator uses a motor to drive a belt or chain to drive a hopper fixed on it. After the hopper is loaded with biomass pellets at the bottom, it rises to the top with the belt or chain, and the biomass pellets are unloaded by centrifugal force or gravity, completing the vertical conveying process.
Parameters of Biomass pellet bucket elevator
| Model | Max feed size(mm) | Capacity(T/H) | Lifting speed(m/s) | Belt width(mm) | Lifting height(m) |
| TD160 | 25 | 5.4-16 | 1.4 | 200 | <40 |
| TD250 | 35 | 12-35 | 1.6 | 300 | |
| TD315 | 45 | 17-40 | 1.6 | 400 | |
| TD400 | 55 | 24-66 | 1.8 | 500 | |
| TD500 | 60 | 38-92 | 1.8 | 600 | |
| TD600 | 70 | 85-142 | 2 | 700 |
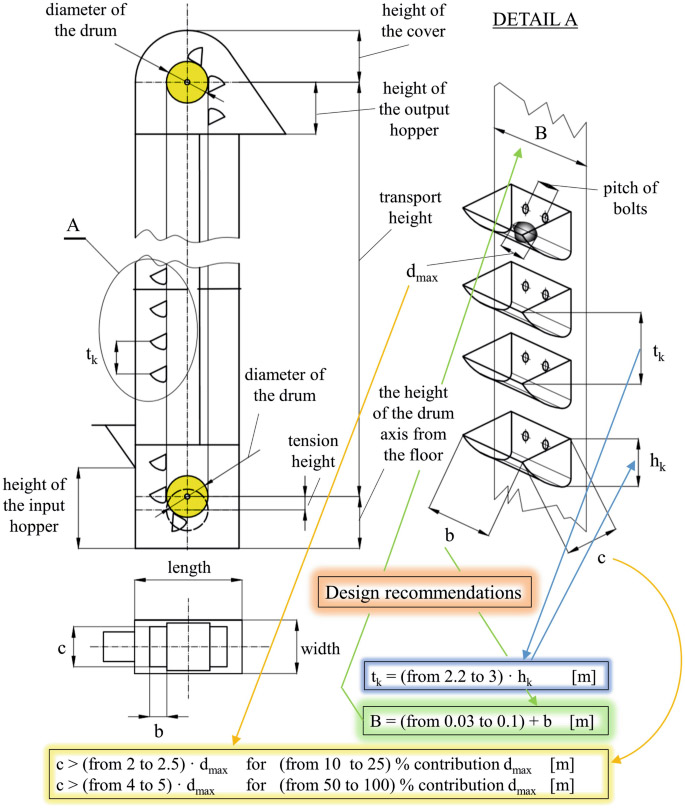
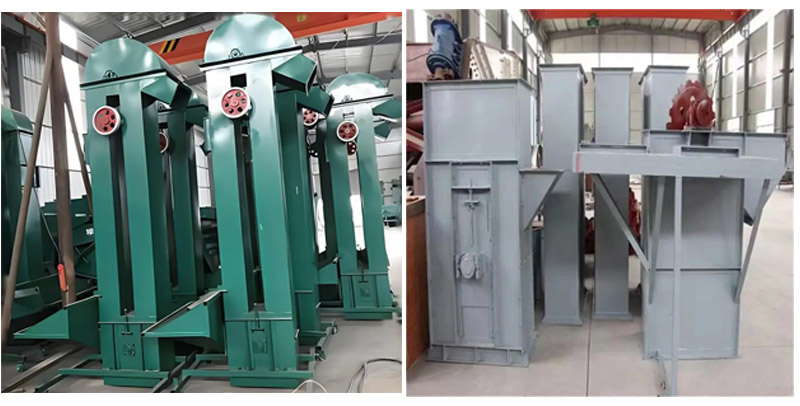
What are the structures of biomass pellet bucket elevator?
Hopper: used to load materials, the material can be plastic, stainless steel or carbon steel.
Belt/chain: used to drive the hopper to move, the chain is suitable for heavy load conditions.
Drive device: includes motor, reducer and drive wheel to provide power.
Casing: closed structure to prevent dust from spilling and material from falling.
Feed port and discharge port: used for material loading and unloading respectively.
Biomass pellet bucket elevator customer case
| Application scenario | Lift height | Lifting capacity | Motor Power | Customer feedback |
| A wood pellet plant in Vietnam with an annual output of 20,000 tons selected our TDTG36/18 biomass pellet bucket elevator to deliver dried wood pellets from the cooler to the finished product warehouse. | 9.6 meters | 6 tons/hour | 3 kW | Smooth and noiseless operation, extremely low particle breakage rate, greatly improving the efficiency of the packaging line. |
| A large biomass energy company in Poland uses our TDTG40/23 bucket elevator to transport pellets pressed from wheat straw, bark, etc. to 4 storage silos. | 12 meters | 10 tons/hour | 4 kW | Multi-point discharge design is adopted, which is compatible with different material particle diameters and meets the needs of multiple categories of warehouse discharge. |
| A customized TDTG50/28 bucket elevator is used in an export-oriented fuel pellet plant in British Columbia, Canada, which is used to vertically transport particles from the underground warehouse to the loading port in the port workshop. | 15 meters | 15 tons/hour | 5.5KW | Fully enclosed structure design, dust and rainproof, adaptable to the complex outdoor environment of the port, and easy equipment maintenance. |

How to choose Biomass pellet bucket elevator?

1. Understand Your Material (Biomass Pellets)
Biomass pellets, such as wood pellets, straw pellets, or feed pellets, have specific properties that influence the choice of bucket elevator:
Particle Size: Ensure the bucket size and spacing are suitable for the pellet diameter.
Density: Biomass pellets are lightweight, so choose a bucket elevator designed for low-density materials.
Fragility: Opt for a gentle handling system to minimize pellet breakage.
Moisture Content: If pellets have high moisture, select corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel.
2. Determine Your Capacity Requirements
Throughput: Calculate the required hourly capacity (e.g., 5-100 tons/hour).
Peak Loads: Consider peak production times to ensure the elevator can handle maximum loads.
3. Choose the Right Type of Bucket Elevator
Centrifugal Discharge: Suitable for fine, free-flowing materials like biomass pellets. Operates at high speeds, ideal for high-capacity applications.
Continuous Discharge: Better for fragile or abrasive materials. Operates at lower speeds, reducing pellet breakage.
4. Select the Appropriate Bucket Design
Bucket Material: Choose plastic, stainless steel, or carbon steel buckets based on the pellet properties and environmental conditions.
Bucket Size and Shape: Ensure the bucket design matches the pellet size and shape for efficient loading and unloading.
5. Consider the Drive System
Belt-Driven: Suitable for lightweight materials like biomass pellets. Offers smooth operation and low maintenance.
Chain-Driven: Ideal for heavy-duty applications or when handling larger volumes.
6. Evaluate the Elevator Height and Layout
Lifting Height: Measure the vertical distance the pellets need to be transported (typically 5-50 meters).
Space Constraints: Ensure the elevator fits within your facility’s layout, including headroom and footprint.
7. Check for Special Features
Dust Control: Biomass pellets can generate dust, so choose an elevator with a sealed design to minimize dust emissions.
Explosion-Proofing: If handling flammable materials, ensure the elevator meets safety standards for explosion prevention.
Corrosion Resistance: For humid or corrosive environments, opt for stainless steel or coated components.


