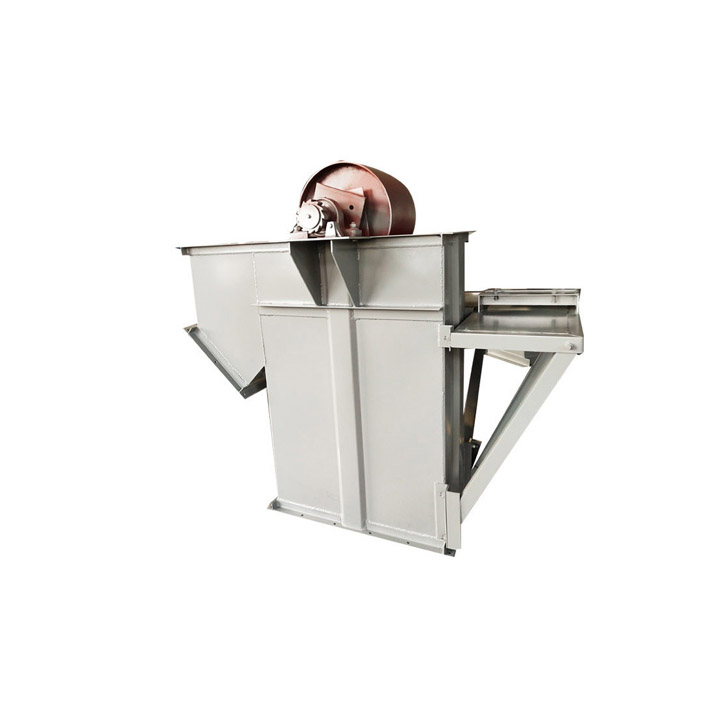
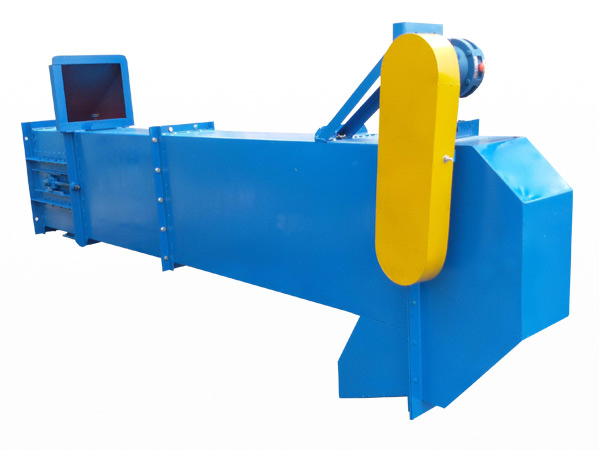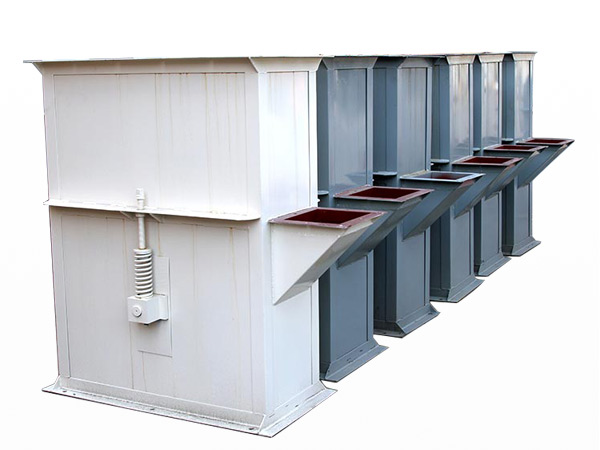
Belt bucket elevator
The rubber belt is a traction component with high strength, inflow feeding, no material spreading, few vulnerable parts, and maintenance costs can be reduced by 80%
Vertically convey powder, granular, and small pieces of loose materials with low abrasiveness
| Lifting height | 40m |
| Conveying capacity | 400m³/h |
| Hopper width | 160-1600 mm |
| Belt Speed | 1-2m/s |
| Material | Carbon steel/stainless steel |
What is a Belt bucket elevator?
A belt bucket elevator is a vertical conveying system designed to transport bulk materials from one level to another using a series of buckets attached to an endless belt. Unlike chain-driven systems, these elevators rely on a reinforced rubber or composite belt to carry buckets, which continuously scoop, lift, and discharge materials. Their robust design and versatility make them a popular choice for industries ranging from building materials to food processing and chemicals.
What is the function of belt bucket elevator?

High Efficiency: Capable of moving large volumes of material vertically with minimal energy consumption.
Gentle Handling: The continuous belt and bucket design ensures smooth material transfer—ideal for fragile or friable materials.
Low Maintenance With fewer moving parts compared to chain systems, belt bucket elevators typically require less maintenance.
Compact Footprint Their vertical design minimizes floor space usage, making them suitable for facilities with limited space.
Customization Options Configurable bucket sizes, belt materials, and drive arrangements allow tailored solutions for various applications.
How does the Belt bucket elevator work?
The bucket belt elevator works like a conveyor belt with buckets: As the belt rotates, the buckets scoop up material at the bottom, carry it to the top, and then tip it out as it turns over. The belt cycles back down to collect more material, creating a continuous lifting process. It is ideal for large-scale lifting on farms, factories, or mines. Its simple design, low maintenance costs, and high capacity make it a popular choice.
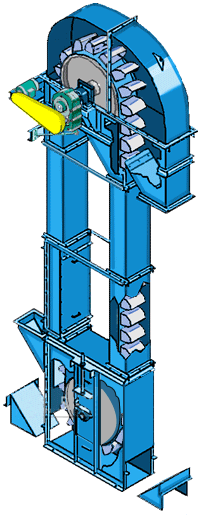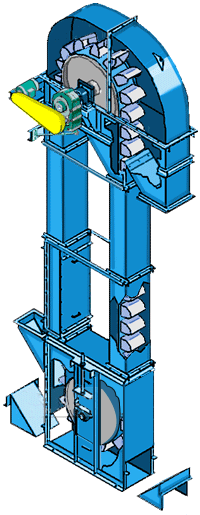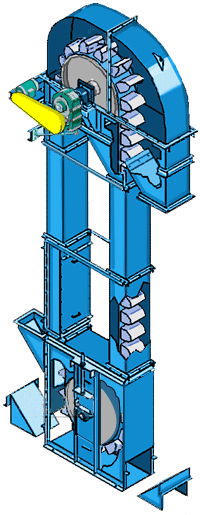
Belt bucket elevator Parameters
| Model | TD160 | TD250 | TD315 | TD400 | ||||||||||||
| Hopper type | Q | h | zD | Sd | Q | h | zD | Sd | Q | h | zD | Sd | Q | h | zD | Sd |
| Conveying volume (m3/h) | 5.4 | 9.6 | 9.6 | 16 | 12 | 22 | 23 | 35 | 17 | 30 | 25 | 40 | 24 | 46 | 41 | 66 |
| Bucket width (mm) | 160 | 250 | 315 | 400 | ||||||||||||
| Dou Rong (L) | 0.5 | 0.9 | 4.2 | 1.9 | 1.3 | 2.2 | 3.0 | 4.6 | 2 | 3.6 | 3.8 | 5.8 | 3.1 | 5.6 | 5.9 | 9.4 |
| Bucket distance (mm) | 280 | 350 | 360 | 450 | 400 | 500 | 480 | 560 | ||||||||
| Bandwidth (mm) | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | ||||||||||||
| Bucket speed (m/s) | 1.4 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.8 | ||||||||||||
| Material quantity (mm) | 25 | 35 | 45 | 55 | ||||||||||||
| Model | TD500 | TD630 | TD160 | TD250 | TD350 | TD450 | ||||||||||
| Hopper form | Q | h | zD | Sd | h | zD | Sd | Q | S | Q | S | Q | S | Q | S | |
| Conveying capacity (m3/h) | 38 | 70 | 58 | 92 | 85 | 89 | 142 | 4.7 | 8 | 18 | 22 | 25 | 42 | 50 | 72 | |
| Bucket width (mm) | 500 | 630 | 160 | 250 | 350 | 450 | ||||||||||
| Dou Rong (L) | 4.8 | 9 | 9.3 | 15 | 14 | 14.6 | 23.5 | 0.65 | 1.1 | 2.6 | 3.2 | 7 | 7.8 | 14.5 | 15 | |
| Bucket distance (mm) | 500 | 625 | 710 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 640 | |||||||||
| Bandwidth (mm) | 600 | 700 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | ||||||||||
| Bucket speed (m/s) | 1.8 | 2 | 1 | 1.25 | 1.25 | 1.25 | ||||||||||
| Material quantity (mm) | 60 | 70 | 25 | 35 | 45 | 55 | ||||||||||
What are the structures of belt bucket elevator?
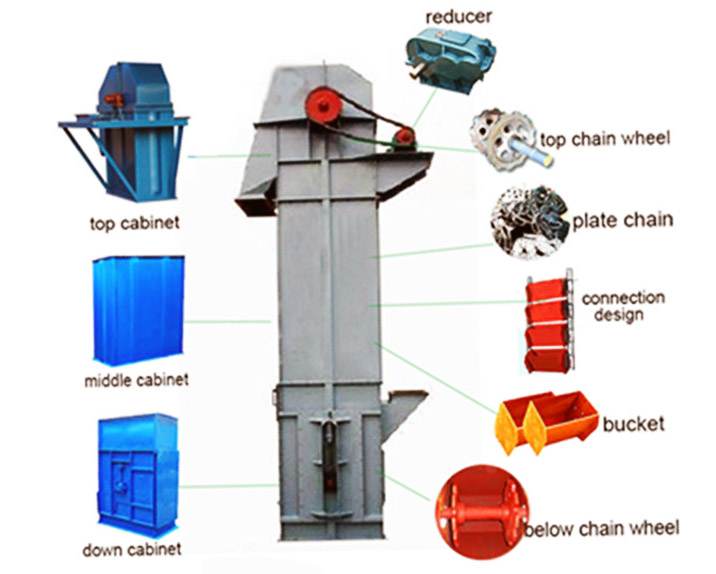
Buckets: Made of materials like reinforced plastic, stainless steel, or mild steel, chosen based on material abrasiveness and chemical properties.
Belt: A rubber or composite belt that attaches to the buckets and transfers them around the pulleys.
Pulleys & Drive Unit: The head (drive) and boot (return) pulleys guide the belt; the head pulley is driven by an electric motor (often via a gear reducer).
Casing: Enclosures protect the moving parts, reduce dust emission, and provide safety access panels.
Tensioning System: Maintains proper tension belt and alignment to prevent slippage and excessive wear.
Support Structure: Robust frames and supports designed to handle vertical loads and vibrations during operation.
What are the applications of belt bucket elevator?

Building Materials: Conveying sand, cement, and aggregates for mixing and construction.
Food Processing & Agriculture: Transporting grains, animal feeds, and delicate food products with minimal damage.
Chemical & Pharmaceutical: Moving bulk chemicals and powders under controlled, hygienic conditions.
Mining & Minerals: Lifting ores and other mineral materials from processing plants or storage silos.
Energy & Power Plants: Conveying coal, fly ash, or other combustion materials in a clean and efficient manner.
Their ability to handle a wide range of materials—from free-flowing to moderately abrasive—makes them an ideal choice across these sectors.
Belt bucket elevator customer case

| Application scenarios | Lift height | Lift capacity | Features |
| Used in new dry process cement production line to lift raw materials from kiln tail to homogenization silo. | 73 meters | 210 m³/h (TGD500 type) | The steel wire rope core belt has high tensile strength and stable operation. Compared with the traditional chain hoist, it saves 20% of electricity and has a service life of more than 5 years |
| Compound fertilizer high tower granulation process, vertically lifting fertilizer particles to the top of the granulation tower. | 100 meters | 767 m³/h (N-TGD1000 type) | A single machine replaces multiple relay lifting, reducing infrastructure costs and energy consumption by 60% |
| Flour mill wheat is vertically transported to the feed inlet of the mill. | 30 meters | 72 m³/h (TD630 model) | Inflow feeding reduces the crushing rate, and the fully sealed structure prevents dust from spilling, suitable for food-grade environments |
How to select a belt bucket elevator?
When choosing a belt bucket elevator, consider the following factors:

| Selection factors | Key parameters/options | Description |
| Material properties | Bulk density (kg/m³) | Light materials (such as grains) can choose shallow buckets, heavy materials (such as ore) require deep buckets; sticky materials require anti-stick coatings; high-temperature materials require heat-resistant tapes. |
| Particle size (mm) | ||
| Humidity/viscosity | ||
| Corrosive/abrasive | ||
| Temperature | ||
| Lifting volume (m/h) | Small flow (<50) | Choose bucket width according to production (such as TD160, TD250, TD630, etc.), large flow requires wide bucket or high-speed design. |
| Medium flow (50~200) | ||
| Large flow (>200) | ||
| Lifting height (m) | Low (<30m) | Ultra-high lifting requires steel wire core tape (such as ST series) or additional tensioning device to prevent belt slippage or breakage. |
| Medium (30~80m) | ||
| High (>80m) | ||
| Motor power (kW) | Low power (<15kW) | Power is positively correlated with lifting amount and height, and resistance (including material weight, friction loss, acceleration, etc.) needs to be calculated. |
| Medium power (15~55kW) | ||
| High power (>55kW) | ||
| Hopper material | Ordinary steel (Q235) | Stainless steel is used for corrosive materials, polyethylene is used for food grade, and wear-resistant steel or ceramic-lined bucket is used for high-wear materials (such as mineral sand). |
| Stainless steel (304/316) | ||
| Nylon/polyethylene | ||
| Wear-resistant steel (NM360) |
Selection Supplementary Notes
Belt type: ordinary rubber belt (<60℃), heat-resistant belt (<120℃), steel cord belt (high strength).
Drive mode: direct-connected reduction motor (low power), hydraulic coupler + reducer (medium and high power, anti-overload).
Safety configuration: backstop (anti-reverse), speed monitor (anti-slip), explosion-proof motor (flammable dust).
Example selection process:
① Determine material characteristics → ② Calculate the required lifting amount → ③ Select bucket type/bandwidth → ④ Check lifting height and power → ⑤ Match materials and safety devices.

