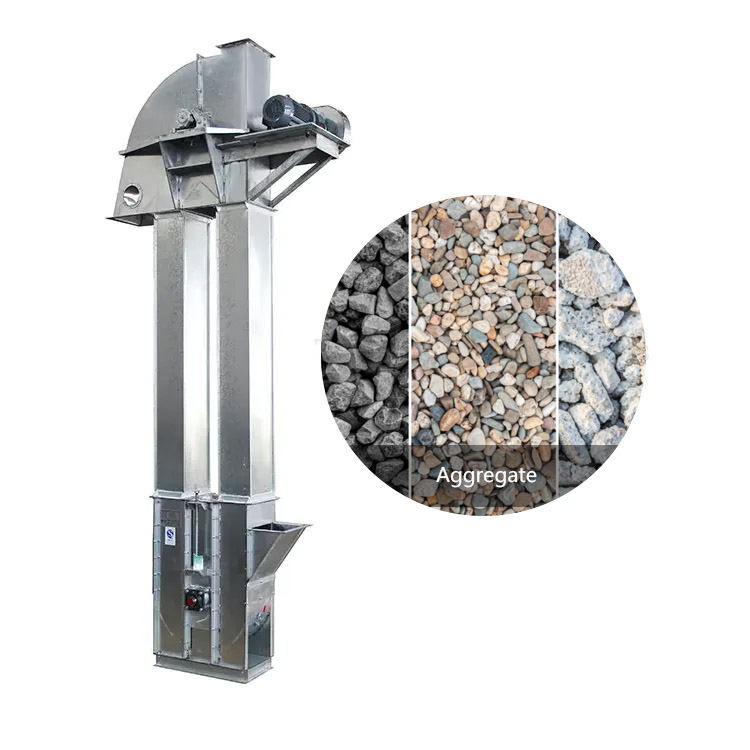
Aggregate Conveying Bucket Elevator
Used to transport bulk materials like aggregates (sand, gravel, crushed stone) efficiently.
| Lifting height | 5-30 m |
| Conveying capacity | 10-100 t/h |
| Hopper capacity | 0.5-5 L |
| Motor power | 2.2-22 kW |
| Operating speed | 1-2 m/s |
What is Aggregate Conveying Bucket Elevator?
Aggregate conveying bucket elevator is a mechanical equipment specially used for vertical conveying of aggregates such as sand, gravel, machine-made sand, slag, etc. It is widely used in industries such as construction, building materials, mining and concrete mixing plants. It lifts aggregates from low to high places through a bucket fixed on a belt or chain, and is suitable for processes such as crushing, screening, storage or loading.

Aggregate Conveying Bucket Elevator Video
What are the applications of Aggregate Conveying Bucket Elevator?
Construction industry: used to convey building materials such as sand, gravel, and concrete.
Mining: conveying ore, coal, etc.
Metallurgy: used to convey metal minerals and alloys.
Chemical industry: conveying chemical raw materials and powders.

Aggregate Conveying Bucket Elevator Customer Case
| Application Scenario | Lifting Amount | Lifting Height |
| Used for vertical lifting of raw materials such as clinker and limestone in cement production lines to ensure continuous feeding to the pre-homogenization yard or mill feed inlet. | 150 tons/hour | 30 meters |
| Used for lifting grains such as wheat and corn in large granaries, transporting them from the ground to the top of the silo for storage or loading. | 80 tons/hour | 25 meters |
| In the sand and gravel crushing and screening system, it is used to lift crushed stone and machine-made sand to the vibrating screen or finished product pile. | 200 tons/hour | 15 meters |

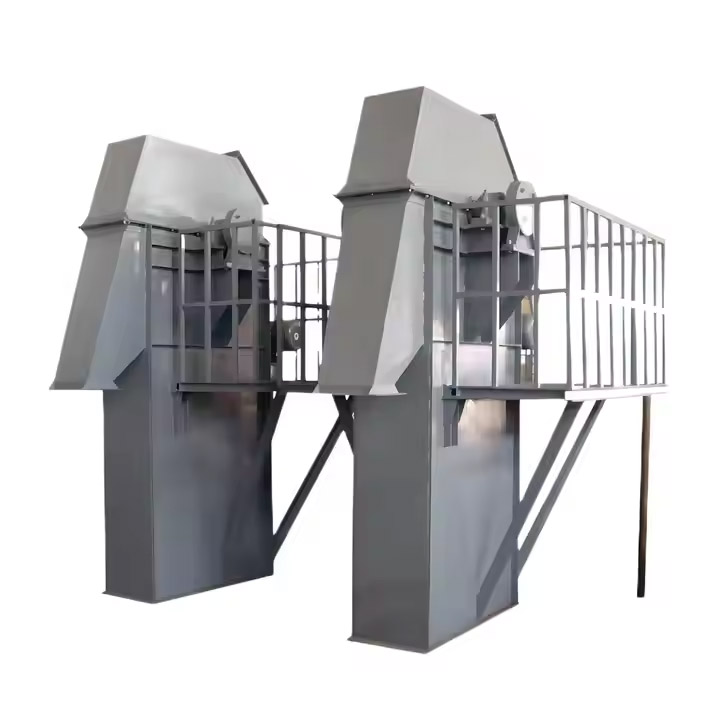
What are the advantages of Aggregate Conveying Bucket Elevator?
High efficiency: suitable for rapid conveying of large quantities of materials.
Space saving: vertical design saves ground space.
Durability: High-strength materials are used to adapt to harsh working environments.
Flexibility: Different heights and conveying capacities can be customized according to needs.
Aggregate Conveying Bucket Elevator Principle
Aggregate Conveying Bucket Elevator drives the lifting belt through the motor, drives the loading bucket to lift the Aggregate from a low place to a high place, and uses gravity and friction to achieve material transportation.
Aggregate Conveying Bucket Elevator Parameters
| Model | Max. Feed Granularity | Capacity | Bucket | Width of Conveyor Belt | |||
| Width | Pitch | Volume | Speed | ||||
| (mm) | (m3/h) | (mm) | (mm) | (L) | (m/s) | (mm) | |
| TD160 | 25 | 5.4-16 | 160 | 280, 350 | 0.5-1.9 | 1.4 | 200 |
| TD250 | 35 | 12-35 | 250 | 360, 450 | 1.3-4.6 | 1.6 | 300 |
| TD315 | 45 | 17-40 | 315 | 400, 500 | 2-5.8 | 1.6 | 400 |
| TD400 | 55 | 24-66 | 400 | 480, 560 | 3.1-9.4 | 1.8 | 500 |
| TD500 | 60 | 38-92 | 500 | 500, 625 | 4.8-15 | 1.8 | 600 |
| TD630 | 70 | 85-142 | 630 | 710 | 14-23.5 | 2 | 700 |
| * More models, support customization, please click here to contact us. | |||||||
What are the structural components of Aggregate Conveying Bucket Elevator?
Lifting bucket: used to load and lift materials.
Lifting belt: connects the bucket and the motor to transmit power.
Frame: supports the entire elevator structure.
Drive system: motor and reducer, providing lifting power.
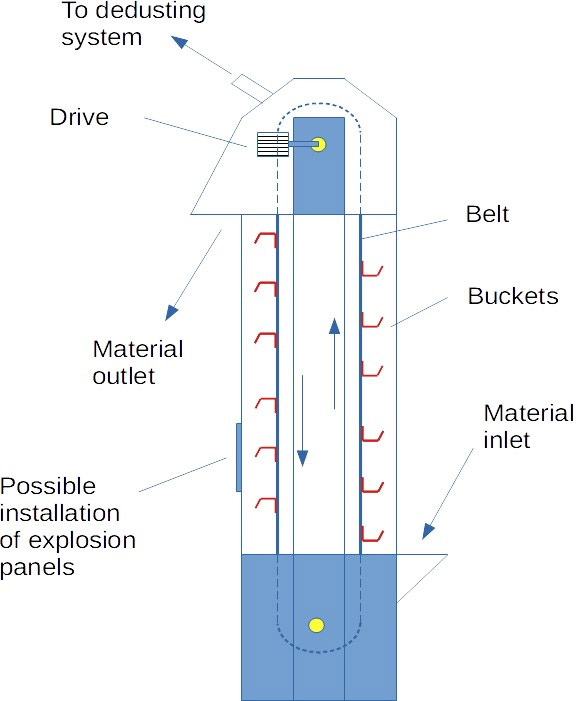
How to select Aggregate Conveying Bucket Elevator?
1. Analysis of aggregate characteristics
The particle size, humidity, hardness and abrasiveness of aggregate directly affect the equipment selection:
| Parameters | Influence of selection | Solution |
| Particle size | Large aggregate (>50mm) is prone to jamming or impact wear | Use deep bucket/sawtooth bucket, chain drive (impact resistant) |
| Moisture | Wet materials are easy to adhere, resulting in incomplete discharge | Choose a stainless steel hopper or anti-stick coating |
| Hardness | High-hardness aggregates (such as granite) accelerate wear | Use wear-resistant steel hoppers or replaceable liners |
| Clay content | Easy to agglomerate and block the hopper | Enlarge the discharge port and add a vibration cleaning device |
2. Lifting capacity
Calculation formula: Lifting capacity (t/h) = single bucket volume (L) × bucket distance (m) × lifting speed (m/s) × filling rate (usually 70-90%)
Selection suggestions:
Small output (<50t/h): light belt bucket elevator (such as NE series).
Medium output (50-300t/h): medium chain bucket elevator (such as TH series).
Large output (>300t/h): heavy plate chain bucket elevator (such as TD series).
3. Lifting height
Below 10m: suitable for short-distance lifting (such as concrete mixing plant).
10-30m: common in sand and gravel aggregate production lines, the structural rigidity needs to be strengthened.
Above 30m: Special design is required (such as dual drive, reinforced chain/belt).
Note: The higher the lifting height, the greater the power requirement, and the tensile strength of the chain/belt needs to be checked.
4. Bucket Material
| Material | Applicable scenarios | Advantages and disadvantages |
| Carbon steel (Q235) | Dry, low-wear aggregate (such as ordinary sand and gravel) | Low cost, but poor wear resistance |
| Wear-resistant steel (NM360) | High wear aggregate (such as granite, iron ore) | Long life, but high price |
| Stainless steel (304/316) | Wet or corrosive environment (such as sea sand, recycled aggregate) | Rust-proof, but high cost and average wear resistance |
| Rubber-lined | Reduce noise and impact (such as glass aggregate) | Shockproof, but poor high temperature resistance |
5. Drive System
| Type | Applicable scenarios | Features |
| Belt drive | Small and medium-sized hoists (<50m), light to medium-loaded aggregates | Smooth operation, low noise, but easy to slip |
| Chain drive | Medium and large hoists (>30m), heavy loads or large aggregates | Impact resistant, but requires regular lubrication and maintenance |
| Dual drive | Ultra-high lifting (>50m) or ultra-large capacity (>500t/h) | Even power distribution, reducing the risk of single point failure |
6. Other key selection factors
Sealing: Aggregates are prone to dust, requiring a fully enclosed housing + dust removal interface (such as a pulse dust collector).
Discharging method:
Centrifugal discharging: suitable for small particles and high-speed lifting (such as sand).
Gravity discharging: suitable for large aggregates (such as crushed stone) and low-speed operation.
Safety device:
Anti-reversal device (to prevent aggregate backflow during shutdown).
Deviation alarm, overload protection.
Selection flow chart
1. Determine the aggregate characteristics (particle size, humidity, hardness) → 2. Calculate the lifting amount → 3. Select the lifting height → 4. Match the hopper material → 5. Select the power type → 6. Configure sealing/safety devices.
If precise selection is required, specific parameters (such as aggregate density, maximum particle size, working conditions) can be provided to further optimize the solution
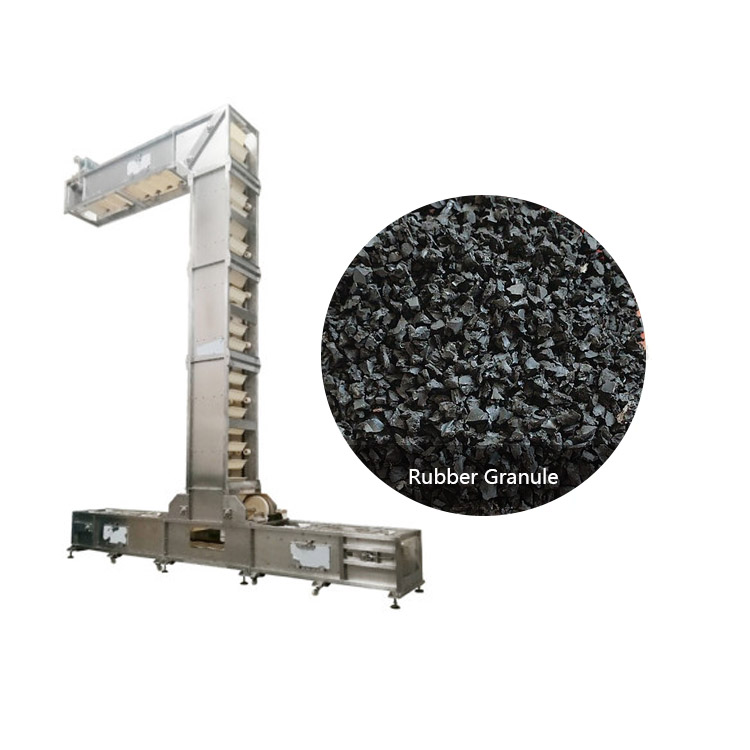

 Chemical Raw Material Bucket Elevator
Chemical Raw Material Bucket Elevator